![[Univ of Cambridge]](http://www.eng.cam.ac.uk/images/house_style/uniban-s.gif)

![[Dept of Engineering]](http://www.eng.cam.ac.uk/images/house_style/engban-s.gif)
![[Univ of Cambridge]](http://www.eng.cam.ac.uk/images/house_style/uniban-s.gif)

![[Dept of Engineering]](http://www.eng.cam.ac.uk/images/house_style/engban-s.gif) |
| INDEX | RESEARCH | PUBLICATIONS | DATABASES | RESUME |
| Current Research (2004-...) |
 |
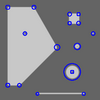
Assisted Video Object Labeling By Joint Tracking of Regions and Keypoints abstract: Manual labeling of objects in videos is a tedious task. We present an approachwhich automatically propagates the labels from a single frame to the next ones. We tackle the challenging problem of tracking segmented regions by combining keypoint tracking with an advanced multiple region matching strategy, based on inclusion similarity and connected regions. We ran experiments on a 101 frame driving video sequence for which we produced the corresponding handlabeled groundtruth. We make this valuable dataset available for the research community. We show our technique can accommodate variations in segmentation (and correct them), even in presence of multiple independent motions and partial occlusion. Results show that most of the labeled pixels can be correctly propagated even after a hundred frames. The performance of this automatic propagation mechanism over many frames can greatly reduce the user effort in the task of video object labeling. keywords: object labeling, segmentation, tracking, matching, computer vision. paper: ICCV07 dataset: CamSeq01 |
 |
Multiscale keypoint detection using the Dual-Tree Complex Wavelet Transform abstract: We present a novel approach to detecting multiscale keypoints using the Dual Tree Complex Wavelet Transform (DTCWT). We show that it is a well-suited basis for this problem as it is directionally selective, smoothly shift invariant, optimally decimated at coarse scales and invertible (no loss of information). Our detection scheme is fast because of the decimated nature of the DTCWT and yet provides accurate and robust keypoint localisation, thanks to the use of the "accumulated energy map". The regularity of this map is used to introduce a new mechanism for robust keypoint scale selection. Keypoints of different nature and size can be detected with limited redundancy, in a way which is consistent with our visual perception. Furthermore results show better robustness against rotation compared to the SIFT detector. keywords: keypoint detection, saliency, multiscale analysis, dual tree complex wavelets, scale selection, computer vision. paper: ICIP06 |
 screenshots |
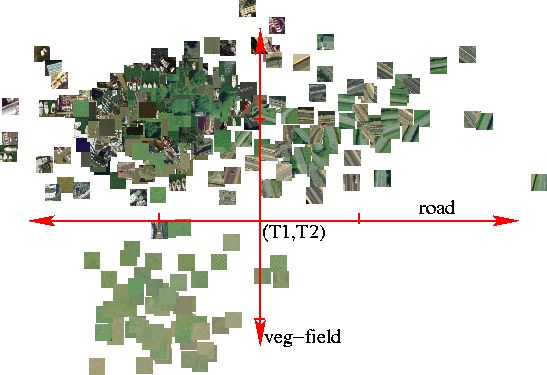
Classification and browsing of remote sensing textures and objects with the Semantic discriminant mapping abstract: We present a new approach based on Discriminant Analysis to map a high dimensional image feature space onto a subspace which has the following advantages: 1. each dimension corresponds to a semantic likelihood, 2. an efficient and simple multiclass classifier is proposed and 3. it is low dimensional. This mapping is learnt from a given set of labeled images with a class groundtruth. In the new space a classifier is naturally derived which performs as well as a linear SVM. We will show that projecting images in this new space provides a database browsing tool which is meaningful to the user. Results are presented on a remote sensing database with eight classes, made available online. The output semantic space is a low dimensional feature space which opens perspectives for other recognition tasks. keywords: supervised dimension reduction, multi-class classification, image browsing, linear discriminant analysis, feature extraction, principal component analysis paper: ICIP05 |
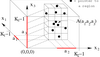 |
Instantaneous mental image search with range queries on multiple region descriptors abstract: The Mental Image Search paradigm allows the user to retrieve images which match the target image s/he has in mind without a starting example. We present a novel approach for this paradigm which enables multiple descriptor range-query, which is necessary to match the more or less precise idea of the user's mental image. Sophisticated query can be formulated in a simple and intuitive way through the query interface which maps directly to the region multifeature space using a grid file index. Images are retrieved instantaneously on a large database. keywords: grid file structure, multiple visual features, large image database, segmented regions, mental image search, query interface, instantaneaous search papers: DELOS05 - technical report |
 |
Interlevel products of complex wavelets abstract: In this paper, we introduce a new multiscale representation for 2-D images named the Inter-Coefficient Product (ICP). The ICP is a decimated pyramid of complex values based on the Dual-Tree Complex Wavelet Transform (DT-CWT). The complex phases of its coefficients correspond to the angles of dominant directional features in their support regions. As a sparse representation of this information, the ICP is relatively simple to calculate and is a computationally efficient representation for subsequent analysis in computer vision activities or large data set analysis. Examples of ICP decomposition show its ability to provide an intuitive representation of multiscale features (such as edges and ridges). Its potential uses are then discussed. keywords: inter-coefficient product, multiresolution analysis, multiscale feature, complex wavelet phase, contour tracking, shift invariance, dominant directions, dual-tree complex wavelets paper: ICIAR05 |
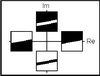 |
Coarse-level object recognition using interlevel products of complex wavelets abstract: This paper introduces the Interlevel Product (ILP) which is a transform based upon the Dual-Tree ComplexWavelet. Coefficients of the ILP have complex values whose magnitudes indicate the amplitude of multilevel features, and whose phases indicate the nature of these features (e.g. ridges vs. edges). In particular, the phases of ILP coefficients are approximately invariant to small shifts in the original images. We accordingly introduce this transform as a solution to coarse scale template matching, where alignment concerns between decimation of a target and decimation of a larger search image can be mitigated, and computational efficiency can be maintained. Furthermore, template matching with ILP coefficients can provide several intuitive “nearmatches” that may be of interest in image retrieval applications. keywords: inter-level product, multiresolution analysis, multiscale feature, complex wavelet phase, cross-scale correlation, shift invariance, characterisation/classification of ridges/edges, dual-tree complex wavelets paper: ICIP05 |
| PhD work (2000-2003) |
| Title: Contributions to Image Retrieval by their Visual Components In november 2003, I obtained my PhD in Computer Science. This work was achieved between 2000 and 2003 at INRIA in IMEDIA group. My PhD page. The following two items cover the main approaches developed during my PhD: |
||
 see PhD page |
Region-Based Image Retrieval: Fast Coarse Segmentation and Fine Color Description abstract: The two major problems raised by a region-based image retrieval system are the automatic detection and visual description of regions. We adopt a coarse detection and fine description approach. In this paper we first present a new method of unsupervised coarse detection which provides intuitive and visually characteristic regions of interest. This segmentation scheme is based on the classification of Local Distributions of Quantized Colors (LDQC). The Competitive Agglomeration classification algorithm is used which has the advantage to automatically determine the number of classes. Then, considering that description must be finer for regions than for images, we propose a new region descriptor of fine color variability: the Adaptive Distribution of Color Shades (ADCS). Combined with an appropriate similarity measure, the high color resolution of ADCS improves the perceptual similarity of retrieved regions compared to existing color descriptors. keywords: image retrieval, region description, segmentation, color quantization, fine color representation, generalised quadratic form distance for color distributions papers: PhD Thesis - JVLC04 - ICIP02 |
 see PhD page |
Mental Image Search by Boolean Composition of Region Categories abstract: Existing content-based image retrieval paradigms almost never address the problem of starting the search, when the user has no starting example image but rather a mental image. We propose a new image retrieval system to allow the user to perform mental image search by formulating boolean composition of region categories. The query interface is a region photometric thesaurus which can be viewed as a visual summary of salient regions available in the database. It is generated from the unsupervised clustering of regions with similar visual content into categories. In this thesaurus, the user simply selects the types of regions which should and should not be present in the mental image (boolean composition). The natural use of inverted tables on the region category labels enables powerful boolean search and very fast retrieval in large image databases. The process of query and search of images relates to that of documents with Google. The indexing scheme is fully unsupervised and the query mode requires minimal user interaction (no example image to provide, no sketch to draw). We demonstrate the feasibility of such a framework to reach the user mental target image with two applications : a photo-agency scenario on Corel Photostock nd a TV news scenario. Perspectives will be proposed for this simple and innovative framework, which should motivate further development in various research areas. keywords: image retrieval, region description, segmentation, color quantization, fine color representation, generalised quadratic form distance for color distributions papers: PhD Thesis - MTAP04 - CBMI03 - ICIP03 |
| |